Mesenteric Artery Disease
Insights and Management
Mesenteric artery disease is a serious condition affecting the arteries that supply blood to the intestines and stomach, vital for digestion. This disease can manifest acutely or chronically, both posing significant health risks.
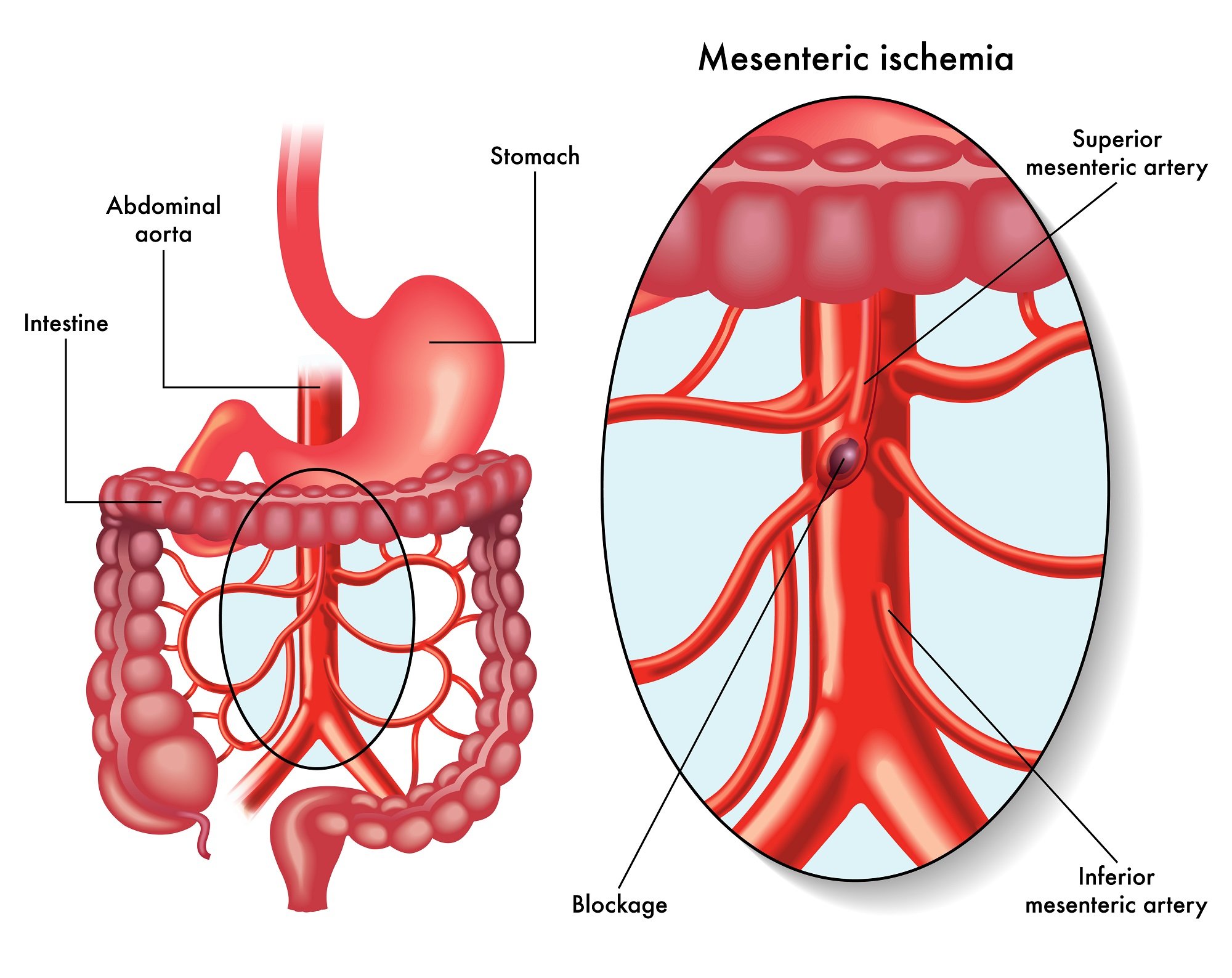
Types of Mesenteric Artery Disease
- Acute Mesenteric Ischemia: This emergency condition occurs when blood flow to the intestines is suddenly blocked, often by a clot. It’s life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
- Chronic Mesenteric Ischemia: Gradually develops over years due to atherosclerosis, leading to narrowed arteries and reduced blood flow to the intestines.
- The Coeliac Trunk Superior Mesenteric Artery, and Inferior Mesenteric Artery are the three main arteries responsible for supplying blood to the small and large intestines.
Causes
- Acute Ischemia: Often caused by clots that originate in the heart, especially in individuals with heart disease or irregular heartbeats
- Chronic Ischemia: Atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries, is the primary cause, slowing blood flow over time.
Symptoms to Watch For
- Acute Mesenteric Ischemia: Sudden, severe abdominal pain.
- Chronic Mesenteric Ischemia: Stomach pain occurring 15–60 minutes after eating, lasting up to 2 hours, and recurring with meals.
Additional symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, fear of eating due to associated pain (food fright), and unintentional weight loss.
Diagnosing Mesenteric Artery Disease
A Computed Tomography (CT) Scan, specifically a CT Angiogram, is the preferred diagnostic test. It produces detailed images that help identify arterial blockages and assess the condition of abdominal organs.
Treatment Approaches
The primary goal is to restore adequate blood flow to the intestines to prevent permanent damage.
- Acute Cases: Emergency Intervention: Rapid action is essential to prevent severe intestinal damage.
Treatments Include:
- Open Surgery: To remove clots and evaluate intestinal health.
- Clot Aspiration: A minimally invasive technique using negative pressure to remove the clot.
- Thrombolytic Therapy: Direct administration of strong blood thinners into the artery to dissolve the clot.
Chronic Cases:
- Minimally Invasive Endovascular Treatment: Often the first-line approach, involving:
- Balloon Angioplasty and Stenting: To widen narrowed arteries and maintain open blood flow.
- Bypass Surgery: A detour is created around the blockage using either one of your veins or a synthetic tube as a graft, restoring adequate blood flow.
Living With and Managing Mesenteric Artery Disease

Preventive measures and lifestyle modifications are critical for managing mesenteric artery disease:
- Avoid smoking to reduce the risk of arterial damage.
- Regular exercise helps maintain vascular health.
- Stay hydrated to support overall bodily functions.
- Manage chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, kidney failure, and heart disease that can exacerbate mesenteric artery disease.
- Follow a heart-healthy diet to reduce atherosclerosis risk.
Prompt recognition of symptoms and immediate medical intervention for acute cases, alongside diligent management of chronic conditions, are key to preventing serious complications associated with mesenteric artery disease.
