Peripheral Arterial Disease(PAD)
Introduction
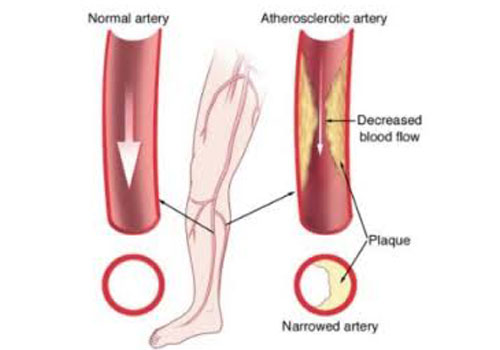
Plaque buildup in the arteries(called atherosclerosis) that carry blood to your head, organs, and limbs.
Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue can harden and narrow the arteries.
Limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood from your heart to your hands, legs, head, kidneys and stomach.
Here we will here focus on P.A.D. that affects blood flow to the legs.
Causes
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High amounts of certain fats and cholesterol in the blood
- Tobacco usage in any form
- High blood pressure
- Inherent blood clotting issues
- Old age
- Obesity
- Idiopathic(unknown)
Eventually, a section of plaque can rupture (break open), causing a blood clot to form at the site
Associated health issues
P.A.D. increases your risk of coronary heart disease, heart attack, stroke, and transient ischemic attack (“mini-stroke”)

Clinical Features
Many people don’t have any signs or symptoms.
Common signs and symptoms are-
- Weak or absent pulses in the legs or feet
- Intermittent Claudication- symptoms when walking or climbing stairs, which may include pain, numbness, aching, or heaviness in the leg muscles. Symptoms also may include cramping in the affected leg(s) and in the buttocks, thighs, calves, and feet.
- Pain in the toe tips even at rest position
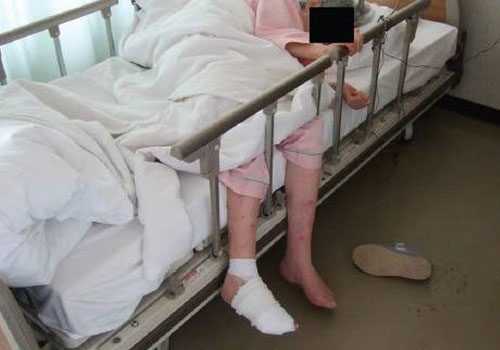
- Sores or wounds on the toes, feet, or legs that heal slowly, poorly, or not at all
- Gangrene (tissue death)- black color change of skin and tissue
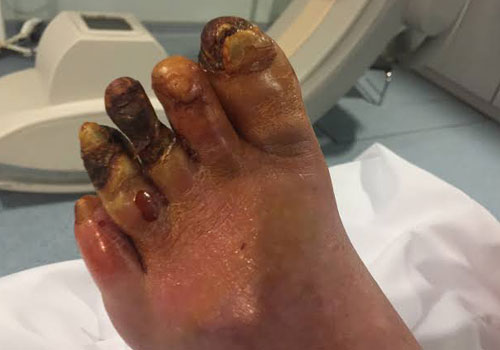
Infected wounds
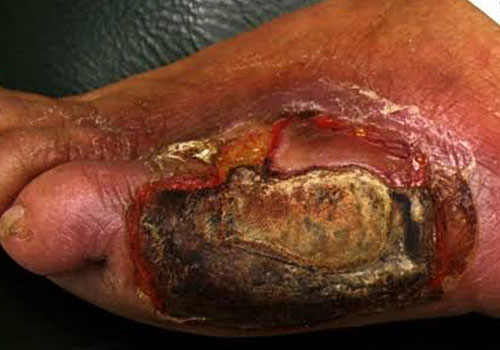
A pale or bluish color to the skin
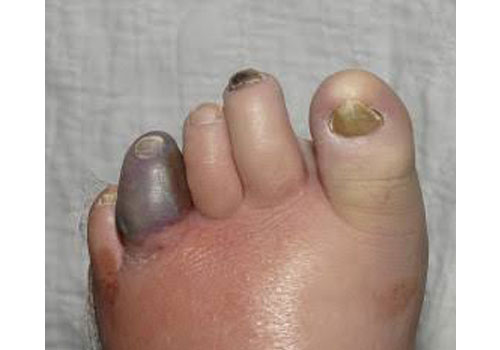
- A lower temperature in one leg compared to the other leg
- Poor nail growth on the toes and decreased hair growth on the legs
- Erectile dysfunction
Diagnostic Tests
- Ankle-Brachial Index(TBI) and Toe Brachial Index(TBI)
Comparing blood pressure in the hands and legs
- Doppler Ultrasound
Provides a early screen regarding presence of reduced blood flow
- Pulse Volume recording
Measuring the pressure based waveforms in the legs
- Treadmill Test
In claudicants, helps to document the distance walked
- Computerised Tomographic Angiogram (CT Scan)
Standard test to obtain information regarding the disease
- Magnetic Resonance Angiogram (MRI Scan)
Standard test to obtain information regarding the disease
Can be done in patients with reduced kidney function
- Angiogram
Invasive test used in patients with doubtful CT/MRI findings
Simultaneous therapy can be done
Treatment
Treatment is based on your signs and symptoms, risk factors, and the results of physical exams and tests.
Overall goals- improving mobility and quality of life, ; reducing symptoms of claudication, reduce infection, heal wounds, reducing risk of heart attack, kidney failure and stroke
Target of treatment in Claudicants- improve walking distance and quality of life
Target of treatment in individuals with wounds/gangrene- remove dead tissue, heal the wound and preserve healthy tissue
Healthy Lifestyle Changes
- Physical activity
- Quitting smoking
- Heart-healthy eating
Treatment options
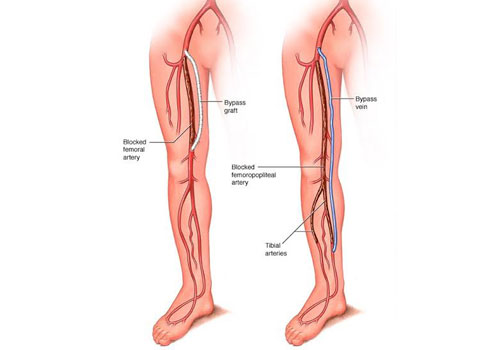
Bypass Grafting Surgery- open surgery
Patients own vein or synthetic tube will be used for bypass
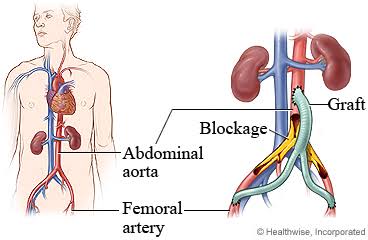
Angioplasty and Stent Placement- minimally invasive
Early recovery compared to open surgery
New devices provide good long term outcomes
Living With Peripheral Artery Disease Symptoms
If you have P.A.D., you may feel pain in your calf or thigh muscles after walking. Try to push as far as you can tolerate the pain and then take a break and allow the pain to ease before walking again. Over time, this may increase the distance that you can walk without pain.
Check your feet and toes regularly for sores or possible infections. Wear comfortable shoes that fit well. Maintain good foot hygiene and have professional medical treatment for corns, bunions, or calluses.
